Jul 28, 2023
Understanding the CIA Triad
The CIA triad stands for Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. It's a foundational concept in information security that outlines the three main objectives of any security strategy:
Confidentiality - ensuring that information is accessible only to those authorized to view it.
Integrity - assuring that data remains accurate, consistent, and unaltered without authorization.
Availability means making sure you can get to your information when you need it.
Let's zoom in on Integrity. It's all about trust. If you're banking online and someone changes the amount in your account without you knowing, that's a big problem. Or, if a doctor is looking at a patient's health records, they need to trust that no one has changed the information. If data gets altered, either by mistake or on purpose, it can cause real harm or confusion. So, integrity keeps our digital world running smoothly and ensures that the information we see and use is accurate and hasn't been tampered with.
Unpacking the Importance of File Integrity Monitoring (FIM)
In our lab, demonstrating Integrity, one of the cornerstones of the CIA Triad, is crucial. Imagine integrity as a safety net ensuring our data is trustworthy and hasn't been tampered with. To show how important and practical this is, we'll use a File Integrity Monitor (FIM).
Think of the FIM as a vigilant guard, always on the lookout. It constantly checks the files we deem important and makes sure they remain in their original, unaltered state. If someone or something tries to change these files - maybe maliciously, or even accidentally - the FIM will notice and immediately alert us.
In our lab setup, as files get altered, the FIM acts as our early warning system. It's a bit like having a smoke detector in your house; if there's a fire, you'll know about it right away. By using FIM, we're giving a practical demonstration of how to uphold data integrity, ensuring our digital information remains trustworthy and reliable.
What we'll learn
In this lab, we'll learn about File Integrity Monitoring (FIM). Think of FIM as a guard for your digital files, always checking they're safe and unchanged. We'll understand why it's important to spot unwanted changes and how FIM helps in maintaining a secure system. By the end, you'll know how to set up FIM and get alerts when something's not right with a file. Throughout this walkthrough, we'll use Josh Madakor's guide as our reference to ensure we understand each step in detail.
Contents
Overview of the Application (Visual Diagram)
FIM Script in Powershell
FIM Script in Python
Code Breakdown
Launching the Demonstration
Conclusion
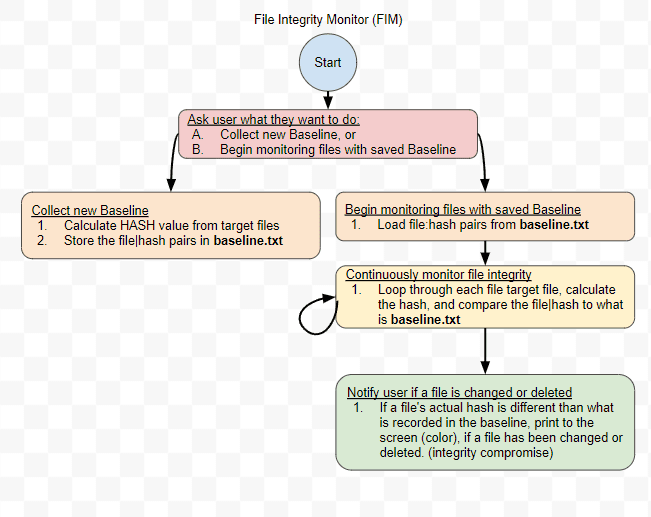
Overview of the Application (Visual Diagram)
FIM Script in Powershell
FIM Script in Python
Code Breakdown
Imports
hashlib: This module implements a common interface to many different secure hash and message digest algorithms.os: Provides a way of using operating system dependent functionality like reading or writing to the file system.time: Allows you to handle time-related tasks. In this script, it's used to introduce a pause.datetime: Used to work with dates and times.
Functions
1. calculate_file_hash
This function computes the SHA-512 hash of a given file (filepath):
It first initializes an empty SHA-512 hash object.
The file is read in binary chunks of size 4096 bytes.
Each chunk is added to the hash object for hashing.
The function returns a tuple with the absolute path of the file and its corresponding SHA-512 hash.
2. erase_baseline_if_already_exists
This function checks if baseline.txt exists in the current directory. If it does, it deletes the file.
3. log_message
This function logs messages to a file named FIM_Log.txt. Each message is prefixed with a timestamp.
Script Logic
Here, the script prompts the user for input on what they'd like to do. They can choose to either:
Collect a new baseline, or
Start monitoring files using an existing baseline.
1. Collecting New Baseline
If the user chooses "A":
The existing baseline file is deleted.
It then lists all files in the
Filesdirectory.For each file, it computes its hash using the
calculate_file_hashfunction.It writes the absolute file path and the computed hash to
baseline.txt.
2. Begin Monitoring
If the user chooses "B", the script does the following:
Reads the
baseline.txtand loads it into a dictionary (file_hash_dictionary), where the key is the file's absolute path, and the value is its hash.The script then enters an infinite loop where it continuously checks the hash of each file in the
Filesdirectory and compares it with the hash in the dictionary.If a file is not in the dictionary, it's considered a newly created file.
If a file's computed hash doesn't match the hash in the dictionary, it's considered changed.
If a file in the dictionary doesn't exist in the directory, it's considered deleted.
Any change detected (creation, modification, or deletion) gets logged to
FIM_Log.txtusing thelog_messagefunction.
In essence, this script is a simple File Integrity Monitoring (FIM) system. It can take a baseline snapshot of files in a directory (by computing their hashes) and then monitor those files for any changes (by continuously comparing current file hashes with the baseline). Any changes are then logged with timestamps to provide a history of file integrity.
Launching the Demonstration
Place your Files directory in C:\Users\Yourprofile\
Create your baseline in either Powershell or Python by running the script and entering A
Monitor the baseline files by running the script and entering B
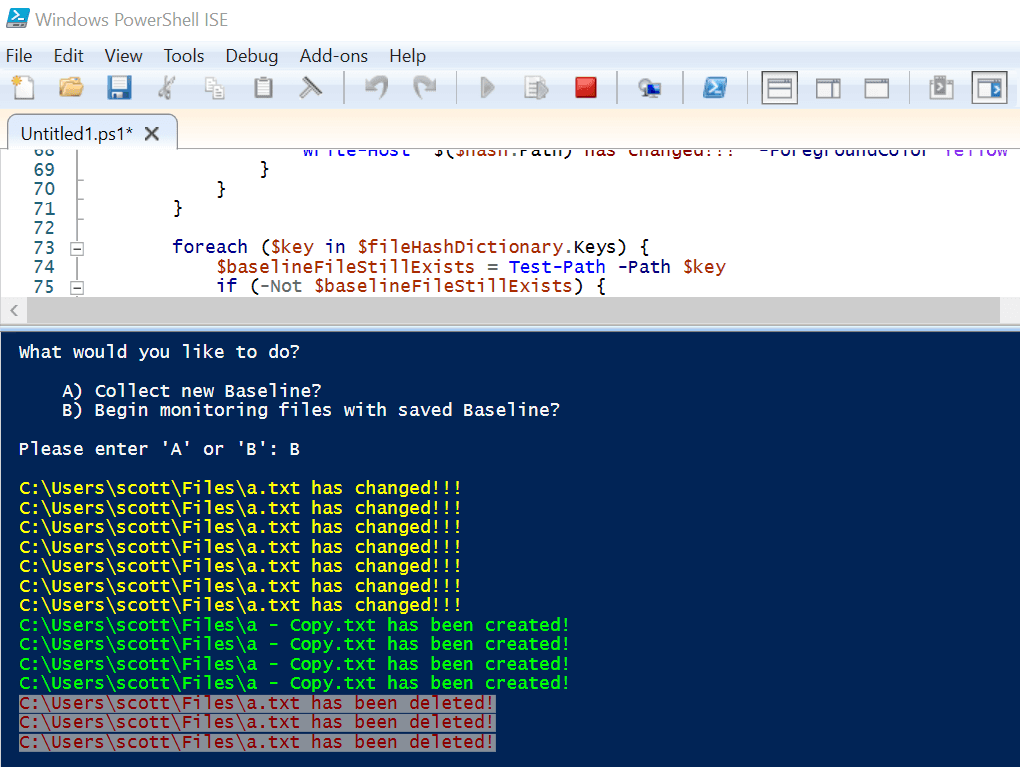
Changes to the directory are highlighted:
Green for new files.
Yellow for changed files.
DarkRed (with Gray background) for deleted files.
If you would like color coded outputs in the terminal for python you can download colorama library. (pip install colorama)
Logging added with time and output created to FIM_Log.
Conclusion
In this FIM (File Integrity Monitoring) project, we developed a tool to continuously monitor and record changes to computer files. By taking an initial 'snapshot' of files and comparing it against their ongoing state, the project identifies any modifications, additions, or deletions. This ensures that files remain genuine and are not tampered with. The application of FIM directly upholds the principle of integrity, as it ensures that data remains consistent and accurate over its lifecycle, guarding against unauthorized changes and potential security breaches. I learned a lot from this project and I hope it gave you a better understanding of how integrity operates at a basic level.